In depth mechanistic biopharmaceutical investigation of oral phospholipid-based formulations for poorly soluble drugs
People involved
Dr. Ann-Christin Jacobsen (Postdoc sponsored by the PRC) - University of Southern Denmark, Odense/Denmark
Dr. Paulina Skupin-Mruglaska (collaborator) - Poznan University of Medical Sciences (see PRC project of Dr. Skupin-Mrugalska)
Abstract
The biopharmaceutical behavior of phospholipid-based enabling formulations of poorly soluble drugs is complex due to the gastrointestinal processing of phospholipids (e.g., enzymatic breakdown)1) and the formation of nano-sized structures (e.g., liposomes and mixed micelles)2). Typically, enabling formulations also induce supersaturation, which further increases complexity.
Experimental evidence indicates that drug solubilized by nano-sized structures and molecularly dissolved drug contribute to oral absorption in different ways: The molecularly dissolved drug determines rate and extent of oral absorption and nano-sized structures may act as a reservoir. Traditional biopharmaceutical tools cannot resolve the distribution of the drug between the molecularly dissolved state and drug associated with nano-sized structures nor the related kinetics.
In this project, a biopharmaceutical approach that can resolve how the drug is distributed between different phases and which nano-sized structures evolve during gastrointestinal processing of phospholipid-based enabling formulations will be established (Figure 1)
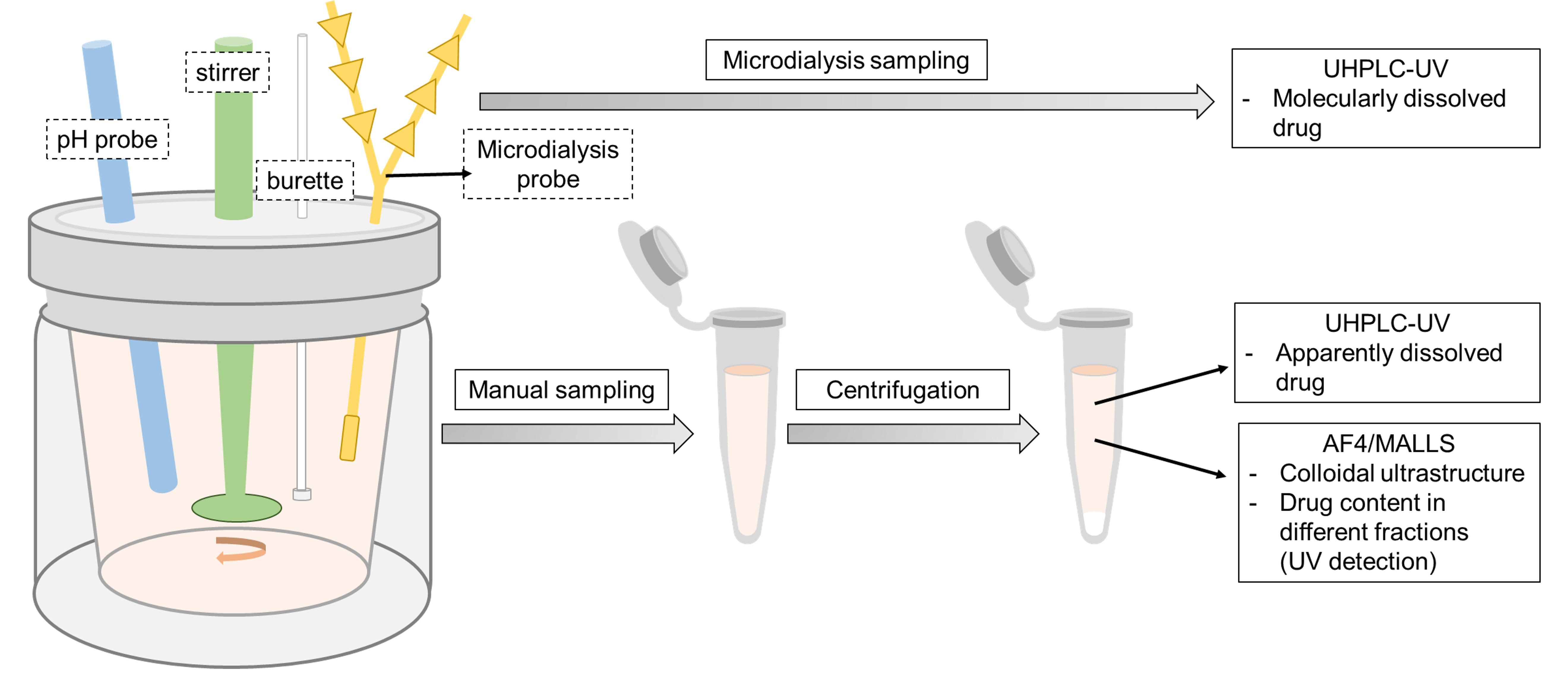
Figure 1. Schematic overview of the proposed biopharmaceutical characterization approach to obtain an in-depth mechanistic understanding of the performance of phospholipid-based oral formulations.
The approach is based on in vitro lipolysis to mimic the gastrointestinal processing1)3) in combination with two innovative tools: (1) microdialysis sampling to determine the molecularly dissolved drug4) and (2) field flow fractionation (AF4/MALLS)2) to resolve the ultrastructural pattern of co-existing colloidal states during lipolysis.
Benefit for the community
A biopharmaceutical approach will be established that combines in vitro lipolysis, microdialysis sampling and AF4-MALLS. This combination is expected to help formulation experts to gain an in-depth mechanistic understanding of the behavior of phospholipid-based enabling formulations in the gastrointestinal tract. Thereby, hopefully, future development of phospholipid-based enabling formulations can be facilitated.
Visit the supervisors lab
Contact to Drug Transport & Delivery at the University of Southern Denmark.
Prof. Martin Brandl and Dr. Ann-Christin Jacobsen.
Exploring the fate of liposomes in the intestine by dynamic in vitro lipolysis
Int. J. Pharm. 437, 253-263
| PubMed |
Co-existing colloidal phases in artificial intestinal fluids assessed by AF4/MALLS and DLS: A systematic study into cholate & (lyso-) phospholipid blends, incorporating celecoxib as a model drug
Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 120, 61-72
| PubMed |
Intrinsic lipolysis rate for systematic design of lipid-based formulations
Drug Delivery Transl. Res.
| PubMed |
Microdialysis and nanofiltration allow to distinguish molecularly dissolved from colloid-associated drug concentrations during biomimetic dissolution testing of supersaturating formulations
Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 174, 106166
| PubMed |
Hydrogenated phospholipid, a promising excipient in amorphous solid dispersions of fenofibrate for oral delivery: Preparation and in-vitro biopharmaceutical characterization
Int. J. Pharm. 644, 123294
| PubMed |