Phospholipids for Pediatric Dosage Forms
Richard Wibel and Peter Hölig, Lipoid GmbH, Frigenstr. 4, D-67065 Ludwigshafen, Germany (email: p.hoelig@lipoid.com)
Safe and Endogenous Compounds for Pharmaceutical Applications
Phospholipids are ubiquitous, endogenous, and nutritional compounds. For pharmaceutical applications, phospholipids are safe and versatile excipients for any administration route. This is demonstrated by their long-standing use in several innovative pediatric drug products and their recognition by regulatory authorities. The excellent tolerability and safety profile of phospholipids is underscored by their presence in breast milk and infant formula, making them one of the first nutrients that infants ingest (Table 1).1)2)
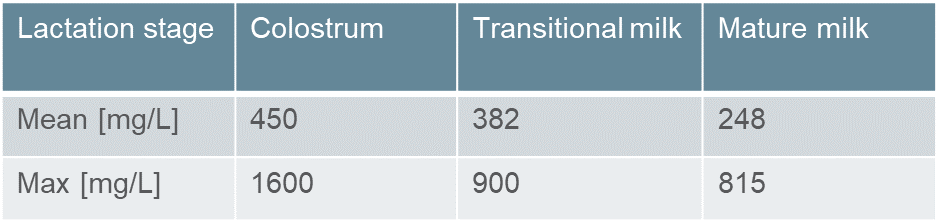
Table 1: Phospholipid content in different stages of human milk.2)
Excipient Selection for Pediatric Drug Products
Formulating drug products for children poses unique challenges. Excipients are key components in the formulation of age-appropriate drug products that are suitable for the envisaged administration route, API, and target age group. In addition to functionality and quality, taste and palatability of the dosage form are typical aspects of drug formulation for children.3) Moreover, particular attention must be paid to excipient safety.4)
As endogenous compounds with an established regulatory framework, phospholipids perfectly fulfil existing safety and quality requirements. Moreover, they provide versatile functionalities and are compatible with a wide range of age-appropriate dosage forms (Figure 1).
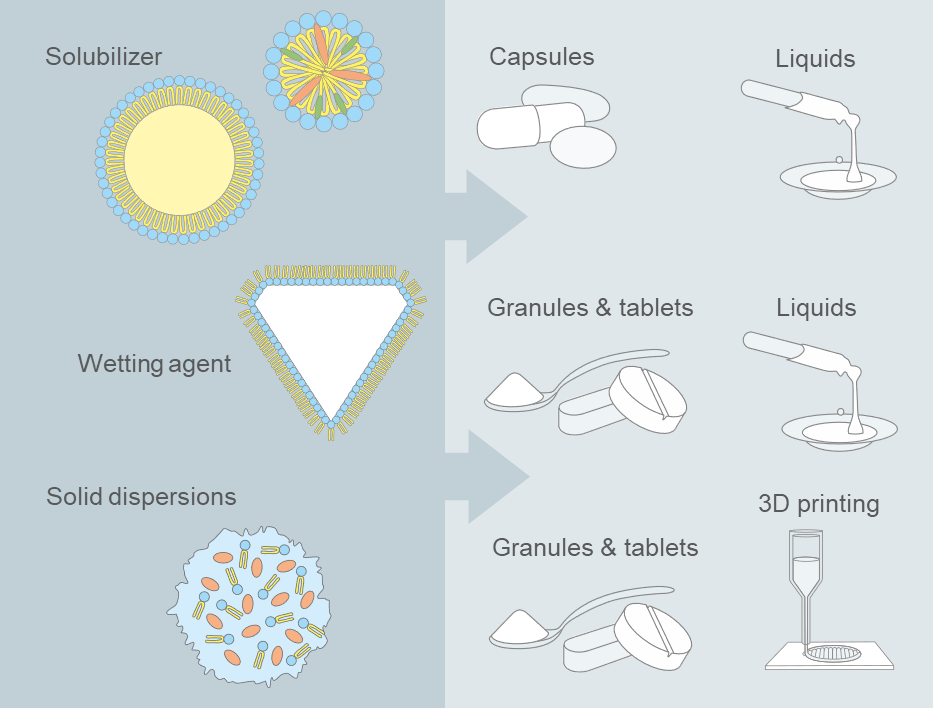
Fig. 1: Selection of phospholipid-based formulation options and their conversion in oral dosage forms.
Concluding Remarks
Regulatory authorities require consideration of pediatric dosage forms early during the product development. The unique needs of children in terms of safety and efficacy must therefore be considered when selecting excipients. Because of their excellent safety profile, multifunctionality, and compatibility with a wide variety of dosage forms, phospholipids are ideally suited for this purpose. Moreover, they allow simultaneous development of pediatric and adult formulations, as well as conversion of adult formulations to pediatric ones without the need to exchange excipients. Various organizations and authorities including WHO, FDA, and EFSA have confirmed the safety of lecithin and phospholipids from a regulatory perspective including their suitability for pediatric formulations.
Opinion on the re-evaluation of lecithins (E 322) as a food additive in foods for infants below 16 weeks of age and follow-up of its re-evaluation as food additive for uses in foods for all population groups
EFSA J. 18, e06266
| PubMed |
Evidence of acceptability of oral paediatric medicines: a review
J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 69, 361-376
| PubMed |
European Paediatric Formulation Initiative (EuPFI)-Formulating Ideas for Better Medicines for Children
AAPS PharmSciTech 18, 257-262
| PubMed |